多时钟交互路径如何检查建立时间和保持时间。
Integer Multiples
设计中经常会定义出现成整数倍数关系的时钟。这样的例子中,我们在相关的时钟(related clocks)中找出公共的时钟周期来进行STA分析。
two clocks are related if they have a data path between their domains
Here is an example that shows four related clocks:
1 | create_clock -name CLKM -period 20 -waveform {0 10} [get_ports CLKM] |
当分析CLKP和CLKM时钟域时,公共的时钟基本周期为20ns,如下图所示。
Integer multiple clocks
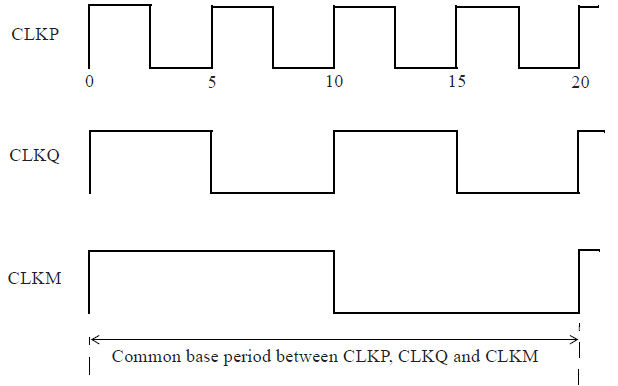
Expanding clock ‘CLKP’ to base period of 20.00 (old period was 5.00, added 6 edges).
Expanding clock ‘CLKQ’ to base period of 20.00 (old period was 10.00, added 2 edges).
简单分析可知,在 CLKP 15ns时刻出发至CLKM 20ns时刻捕获进行setup time check 最为严苛。而在CLKP&CLKM 0ns时刻进行hold time check最为合理。时序报告这里不再贴出。
Non-Integer Multiples
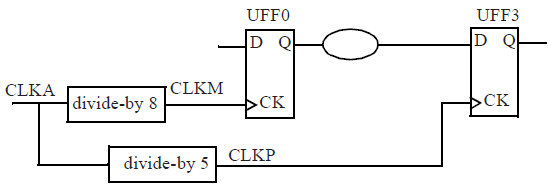
考虑数据路径中两个clock domains的频率不成倍数关系时,例如,the launch
clock is divide-by-8 of a common clock and the capture clock is divide-by-5
of the common clock ,如下图所示。
Non-integer multiple clocks
时钟定义指令如下:
1 | create_clock -name CLKM -period 8 -waveform {0 4} [get_ports CLKM] |
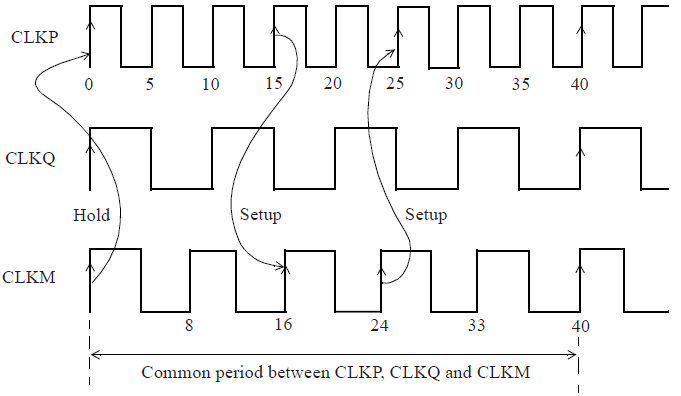
STA分析时需寻找related clock的common period。例如,common period 分别有CLKQ&CLKP:10ns,CLKM&CLKQ:40ns,CLKM&CLKP:40ns。
下面考虑CLKM clock domain 和CLKP clock domain,公共的周期为40ns。
Expanding clock ‘CLKM’ to base period of 40.00 (old period was 8.00, added 8 edges).
Expanding clock ‘CLKP’ to base period of 40.00 (old period was 5.00, added 14 edges).
Setup and hold checks for non-integer multiple clocks
setup check 中必须要满足launch edge和capture edge 的clock最小时间要求。
-
如果时序路径由CLKM 到CLKP,则在CLKM 24ns launch ,CLKP 25ns时capture最严苛;
-
如果时序路径由CLKP到CLKM,在CLKP 15ns,CLKM 16ns 时最严苛。
hold check中时钟是在0ns时刻检查最严苛。
时序报告在此不一一列出。
Phase Shifted
下面两个时钟相差90度相移。
1 | create_clock -period 2.0 -waveform {0 1.0} [get_ports CKM] |
Phase-shifted clocks

对于setup time 而言,数据在CKM 0ns建立,于CKM90 0.5ns时进行建立时间检查。
对于hold check而言,我们得在建立时间检查中capture edge 的前一个周期时刻点进行检查。例如在launch 2ns时刻,此时于2.5ns时刻进行setup check,因此在前一个capture edge 0.5ns时刻进行hold check。
因此该例中对于hold check 是十分有利的,因为hold time check中,数据捕获路径clock的时刻早于数据建立clock的时间。
Half-Cycle Paths
设计中同时存在negative-edge triggered flip-flops(active clock edge is falling edge)和positive-edge triggered flip-flops (active clock edge is rising edge)时,就可能属于half-cycle paths。
A half-cycle path could be from a rising edge flip-flop to a falling edge flip-flop, or vice versa.
A half-cycle path
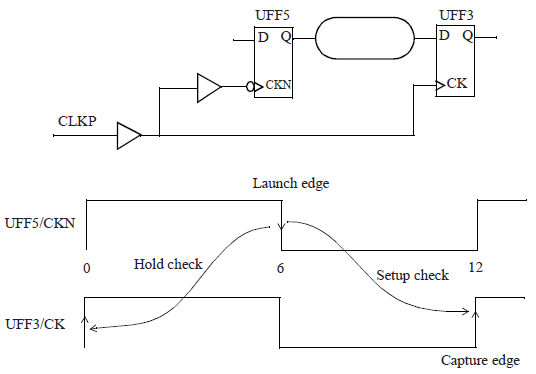
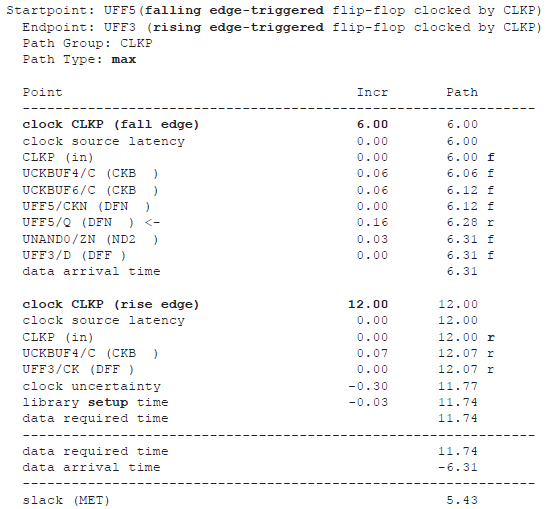
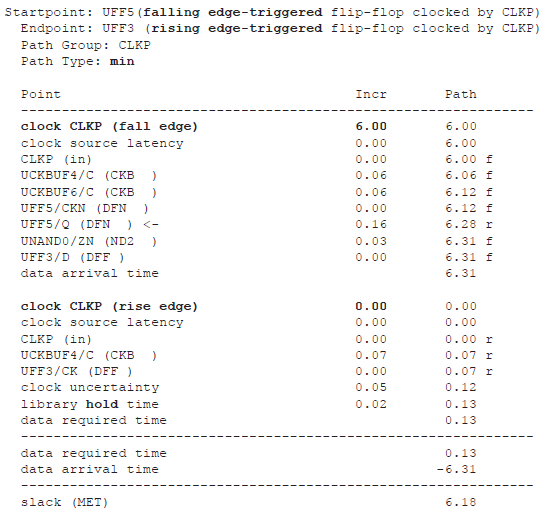
下降沿出现在6ns时刻,上升沿在12ns时刻。因此,数据经过半个时钟周期,6ns,传输到捕获路径触发器 ,在半个时钟周期内进行建立时间检查。
保持时间检查中,通常于捕获边沿的前一个时钟周期检查。因此,12ns时刻捕获,前一个捕获边沿是0ns时刻。这样,实际上为保持时间检查增加了half-cycle margin,使保持检查结果有很大的positive slack。
the setup timing check path report
the hold timing path
False Path
电路中某些timing paths有可能是不存在或者在设计中没有实际作用的。这些路径我们可以设置为false paths,使得STA在分析过程中忽略掉。
False paths的例子:
- from one clock domain to another clock domain;
- from a clock pin of a flip-flop to the input of another flip-flop;
- through a pin of a cell;
- through pins of multiple cells;
- or a combination of these
A false path is set using the set_false_path specification. Here are some examples.
1 | set_false_path -from [get_clocks SCAN_CLK] \ |
Few recommendations on setting false paths are given below.
To set a false path between two clock domains, use:
1 | set_false_path -from [get_clocks clockA] \ |
instead of:
1 | set_false_path -from [get_pins {regA_*}/CP] \ |
The second form is much slower.
Another recommendation is to minimize the usage of -through options, as it adds unnecessary runtime complexity. The -through option should only be used where it is absolutely necessary and there is no alternate way to specify the false path.
From an optimization perspective, another guideline is to not use a false path when a multicycle path is the real intent. If a signal is sampled at a known or predictable time, no matter how far out, a multicycle path specification should be used so that the path has some constraint and gets optimized to meet the multicycle constraint.
Reference:
1.Static Timing Analysis for Nanometer Designs A Practical Approach

