主要分析单周期时序路径下setup/hold time check
单周期路径下setup time check
Input to Flip-flop Path
时序报告:
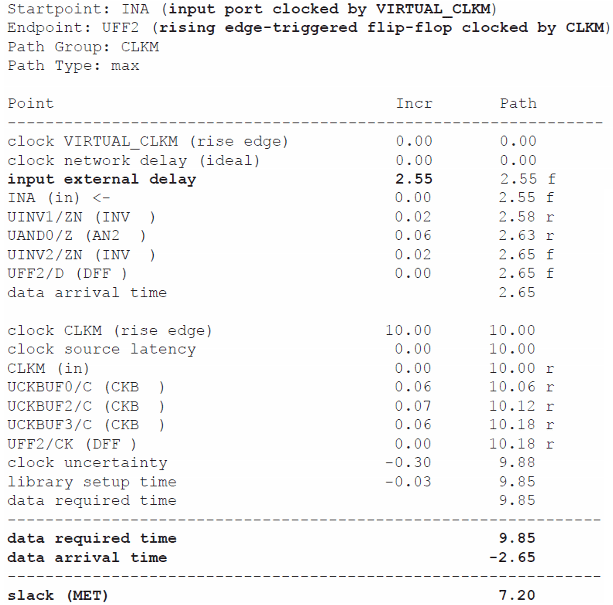
input port clocked by VIRTUAL_CLKM,可以认为是由一个在设计外面的imaginary(virtual)flip-flop驱动的input port。另外,从该clock pin到达input port INA的max delay 可以被定义为一个确定的数值,在报告中为input external delay。通过以下SDC commands可以实现上述操作:
1 | create_clock -name VIRTUAL_CLKM -period 10 -waveform {0 5} |
同时可以注意到DUA中经过input port INA,和其连接的第一个cell UINV1,可以通过specifying the driving cell of the input port INA计算delay:
1 | set_driving_cell -lib_cell BUFF -library lib013lwc [get_ports INA] |
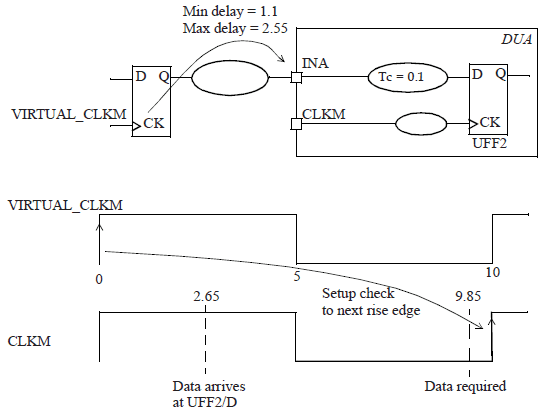
Setup check for the path through input port
Flip-flop to Output Path
类似于input port 约束,output port 也可以受virtual clock,internal clock of the design,input clock port,output clock port约束。下面是output pin ROUT constraint with respect to a virtual clock。如下:
1 | set_output_delay -clock VIRTUAL_CLKP -max 5.1 [get_ports ROUT] |
To determine the delay of the last cell connected to the output port correctly,one needs to specify the load on this port.
The output load is specified above using the set_load command.
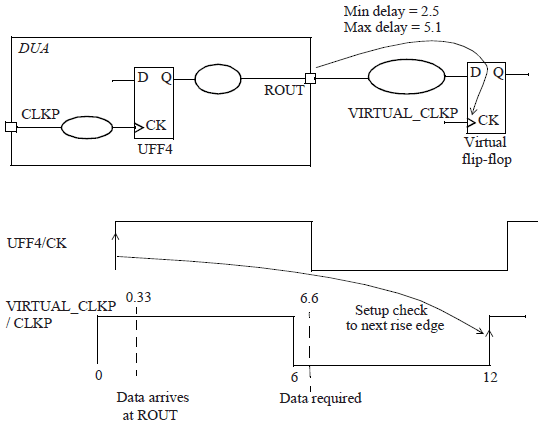
Setup check for path through output port
时序报告:
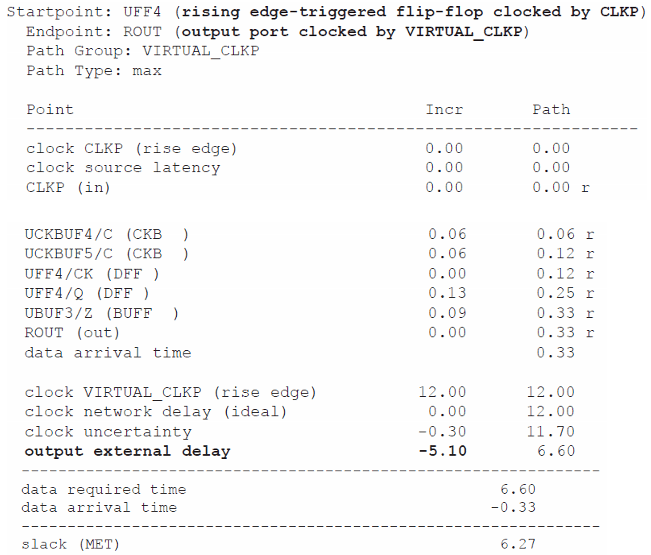
Notice that the output delay specified appears as output external delay and behaves like a required setup time for the virtual flip-flop
因为 output external delay应该对应于virtual flip-flop的launch path中,但此处路径已在ROUT终止,因此将其放于capture path中,表现为负值。
总结:
slack = (Tcapture + Tcycle - Tuncertainty - Tsetup - Toutput_dealy)- (Tlaunch + Tck2q + Tdp)
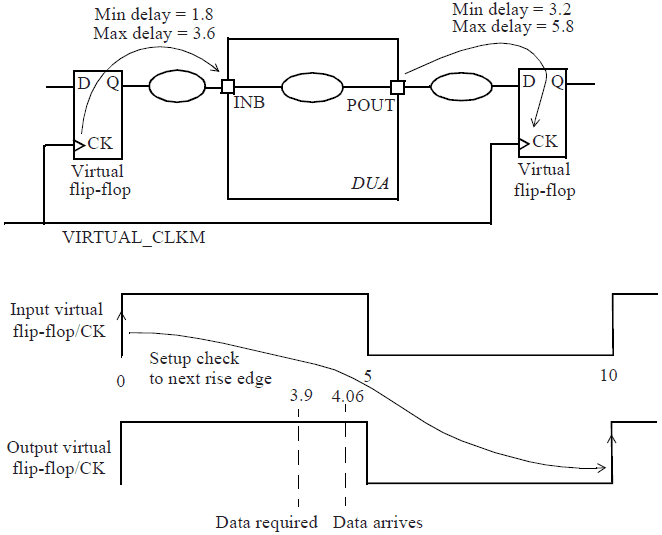
Input to Output Path
和先前input path、output path类似,使用Virtual clocks来约束input&output ports。通过以下指令进行约束:
1 | set_input_delay -clock VIRTUAL_CLKM -max 3.6 [get_ports INB] |
Combinational path from input to output port
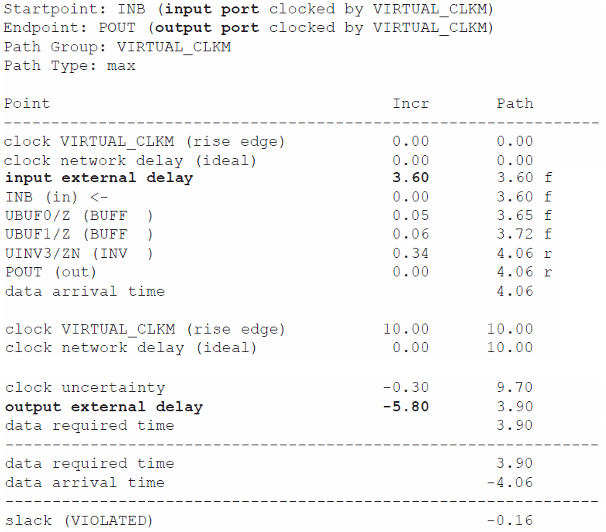
时序报告:
单周期路径下hold time check
Hold timing check确保使flip-flop能够捕获其原始的正确数据,保证前一级flip-flop输出值变化不会经过capture flip-flop,覆盖输出数据 。
Hold time 要求flip-flop在时钟的有效沿之后的指定时间段内,被锁存的数据应保持稳定。
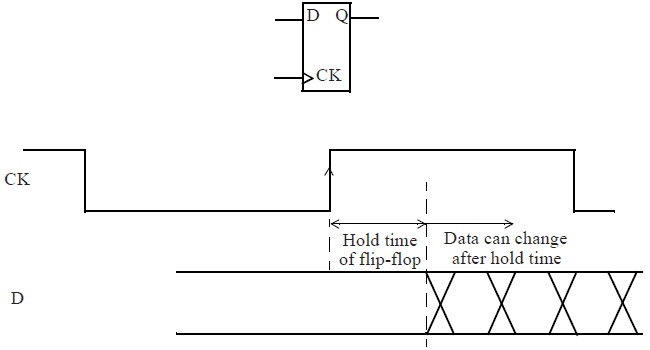
hold timing check 和setup timing check 有如下差别:
The hold check is from one active edge of the clock in the launch flip-flop to the same clock edge at the capture flip-flop.
Thus, a hold check is independent of the clock period.
The hold check is carried out on each active edge of the clock of the capture flip-flop.
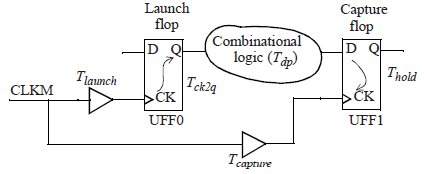
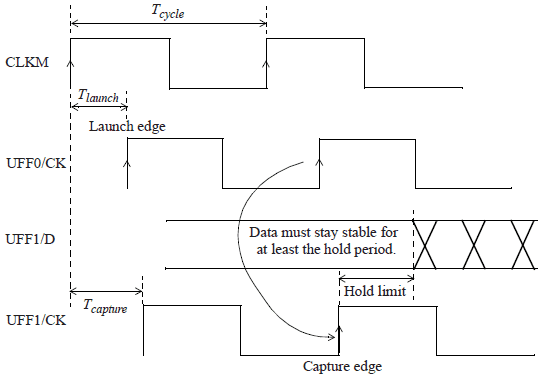
The hold check can be mathematically expressed as:
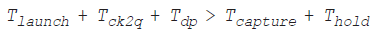
Slack = (Tlaunch + Tck2q + Tdp) - (Tcapture + Thold)
Hold time check 对capture flip-flop上数据引脚的路径施加了下限或最小值限制。需要确定到捕获触发器D引脚的最快路径。 这意味着将始终使用最短路径来验证hold checks。 因此,通常在fast timing corner 中执行hold checks。
Hold time check 和setup time check 之间的关系
如下图所示,hold timing check 确保:
- Data from the subsequent launch edge must not be captured by the setup receiving edge.
- Data from the setup launch edge must not be captured by the preceding receiving edge.
Two hold checks for one setup check
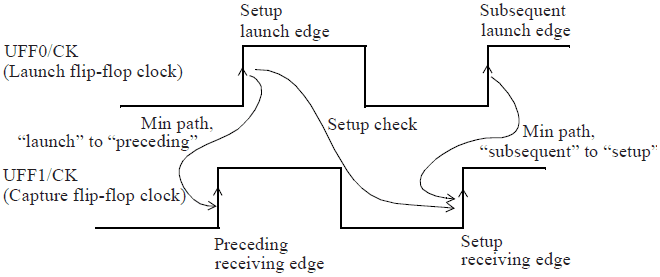
UFF0 :launch flip-flop,UFF1:capture flip-flop
Setup check:setup launch edge --> setup receiving edge
The subsequent launch edge must not propagate data so fast that the setup receiving edge does not have time to capture its data reliably.
The setup launch edge must not propagate data so fast that the preceding receiving edge does not get a chance to capture its data.
While setup violations can cause the operating frequency of the design to be lowered, the hold violations can kill a design, that is, make the design inoperable at any frequency. Thus it is very important to understand the hold timing checks and resolve any violations.
Reference:
1.Static Timing Analysis for Nanometer Designs A Practical Approach

